
Databases are the Holy Grail for hackers, and as such, must be protected with utmost care. This is the first in a series of articles in which we’ll give an overview of best practices for securing your databases with security best practices. We’re starting with one of the most popular open-source databases, PostgreSQL, and will go over several levels of security you’d need to think about:
In the ideal world, your PostgreSQL server would be completely isolated and not allow any inbound connections, SSH or psql. Unfortunately, this sort of air-gapped setup is not something PostgreSQL supports out-of-the-box.
The next best thing you can do to improve the security of your database server is to lock down the port-level access to the node where the database is running with a firewall. By default, PostgreSQL listens on a TCP port 5432. Depending on the operating system, there may be different ways to block other ports. But using Linux’s most widely available iptables firewall utility, the following will do the trick:
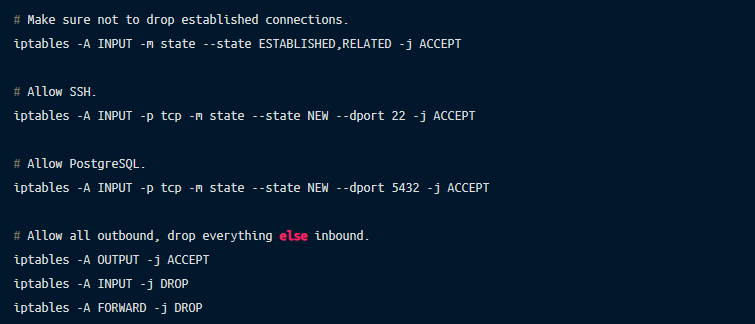
Note: When updating the iptables rules, it is a good idea to use the iptables-apply tool which automatically rolls back the changes in case you lock yourself out.
The PostgreSQL rule above will allow anyone to connect to port 5432. You could make it more strict by only accepting connections from certain IP addresses or subnets:

Going back to our ideal scenario, being able to entirely prevent inbound connections to port 5432 would require a some sort of a local agent that maintains a persistent outbound connection to the client node(-s) and has the ability to proxy traffic to the local PostgreSQL instance.
This technique is called “reverse tunneling” and can be demonstrated using SSH remote port forwarding feature. You can open up a reverse tunnel by running the following command from the node where your PostgreSQL database is running:
Of course, the <client-host> should be accessible from the PostgreSQL node and have the SSH daemon running. The command will forward the port 5432 on the database server to the port 5432 on the client machine, and you will be able to connect to the database over the tunnel:
listen_addressesIt is a good practice to restrict addresses on which the server is listening for client connections using the listen_addresses configuration file directive. If the node PostgreSQL is running on has multiple network interfaces, use it to make sure the server is only listening on the interface(-s) over which the clients will be connecting to it:
If the clients connecting to the database always reside on the same node (or, say, co-located in the same Kubernetes pod with PostgreSQL running as a side-car container), disabling TCP socket listening can completely eliminate network from the picture. Setting listen addresses to an empty string makes the server accept only Unix-domain socket connections:
With the majority of the world’s web moving to HTTPs, there’s little excuse for not using a strong transport encryption for database connections as well. PostgreSQL supports TLS (which is still referred to as SSL in the documentation, configuration and CLI for legacy reasons) natively and provides ways to use it for both server and client authentication.
For server authentication, you first need to obtain a certificate the server will present to the connecting clients. Let’s Encrypt makes it really easy to get free X.509 certificates, for example using the certbot CLI tool:
Keep in mind that by default certbot uses HTTP-01 ACME challenge to validate the certificate request which requires a valid DNS for the requested domain pointing to the node and port 80 to be open.
If you can’t use Let’s Encrypt for some reason and want to generate all secrets locally, you can do it using openssl CLI tool:
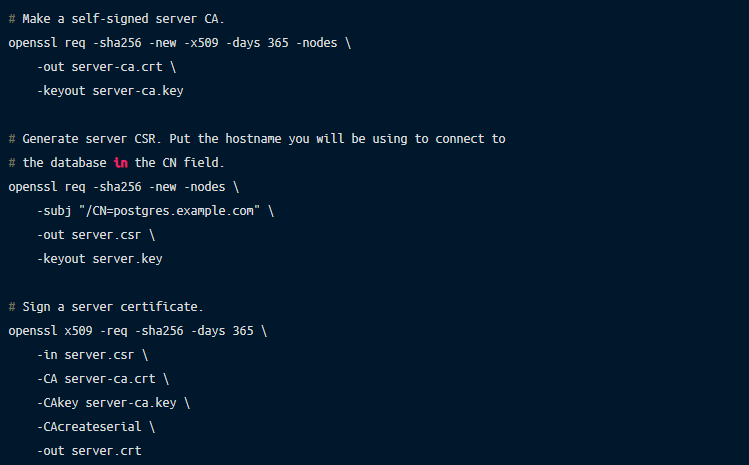
Of course, in the production environment you’d want to make sure that these certificates are updated prior to their expiration date.
There are a range of authentication methods you can use when connecting to a Postgres Database. We recommend using client certificates. Client certificate authentication allows the server to verify the identity of a connecting client by validating that the X.509 certificate presented by the client is signed by a trusted certificate authority.
It’s a good idea to use different certificate authorities to issue client and server certificates, so let’s create a client CA and use it to sign a client certificate:
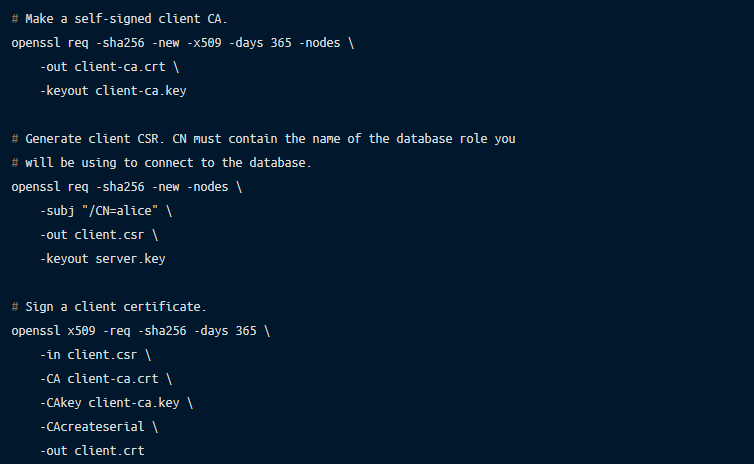
Note that the CommonName (CN) field of the client certificate must contain the name of the database account the client is connecting to. PostgreSQL server will use it to establish the identity of the client.
Getting all the pieces together, you can now configure the PostgreSQL server postgresql.conf to accept TLS connections:
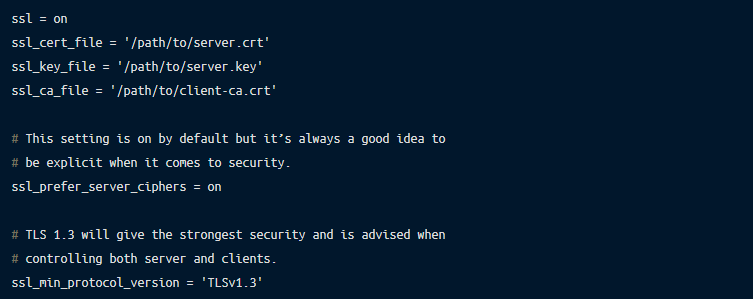
One last remaining bit of configuration is to update the PostgreSQL server host-based authentication file, the pg_hba.conf to require TLS for all connections and authenticate the clients using X.509 certificates:
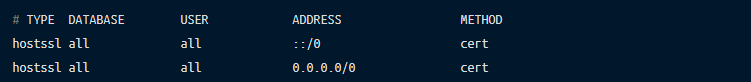
Now, clients connecting to the database server will have to present a valid certificate signed by the client certificate authority:
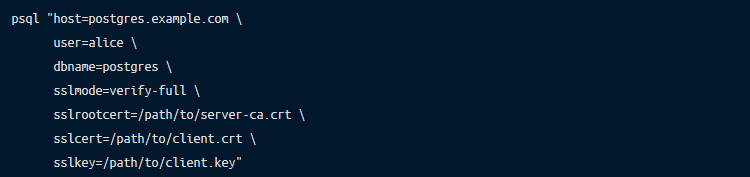
Note that by default psql will not perform the server certificate validation so “sslmode” must be set to verify-full or verify-ca, depending on whether you’re connecting to the PostgreSQL server using the same hostname as encoded in its X.509 certificate’s CN field.
To reduce the command verbosity and not have to enter the paths to TLS secrets every time you want to connect to a database, you can use a PostgreSQL connection service file. It allows you to group connection parameters into “services” which can then be referred to in the connection string via a “service” parameter.
Create ~/.pg_service.conf with the following content:

Now, when connecting to a database, you’d only need to specify the service name and the name of the database you want to connect to:
So far we have explored how to protect the PostgreSQL database server from unauthorized network connections, use strong transport encryption and make sure that server and clients can trust each other’s identities with mutual TLS authentication. Another piece of the puzzle is to figure out what users can do and what they have access to once they’ve connected to the database and had their identity verified. This is usually referred to as authorization or access controls.
PostgreSQL has a comprehensive user permissions system that is built around the concept of roles. In modern PostgreSQL versions (8.1 and newer) a “role” is synonymous with “user” so any database account name you use, say, with psql (e.g. “user=alice”) is actually a role with a LOGIN attribute that lets it connect to a database. In fact, the following SQL commands are equivalent:

Besides the ability to log in, roles can have other attributes that allow them to bypass all permission checks (SUPERUSER), create databases (CREATEDB), create other roles (CREATEROLE), and others.
In addition to attributes, roles can be granted permissions which can be split in two categories: membership in other roles and database object privileges. Let’s take a look at how these work in action.
For our imaginary example, we will be tracking the server inventory:

By default, PostgreSQL installation includes a superuser role (usually called “postgres”) used to bootstrap the database. Using this role for all database operations would be equivalent to always using “root” login on Linux, which is never a good idea. Instead, let’s create an unprivileged role and assign permissions to it as needed following the principle of least privilege.
Rather than assigning privileges to each new user/role individually, you can create a “group role” and grant other roles (mapping onto individual users) membership in this group. Say, you want to allow your developers, Alice and Bob, to view the server inventory but not modify it:
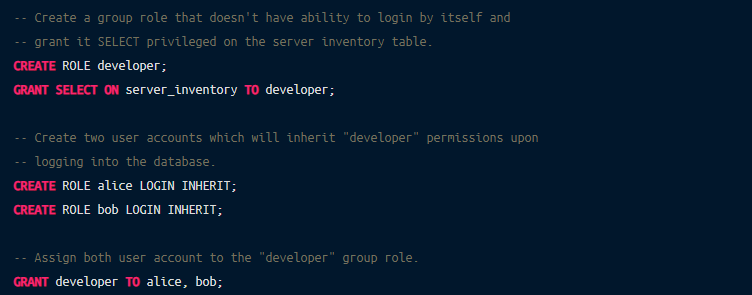
Now, when connected to the database, both Alice and Bob will inherit privileges of the “developer” group role and be able to run queries on the server inventory.
The SELECT privilege applies to all table columns by default, though it doesn’t have to. Say, you only wanted to allow your interns to view the general server inventory information without letting them connect by hiding the IP address:
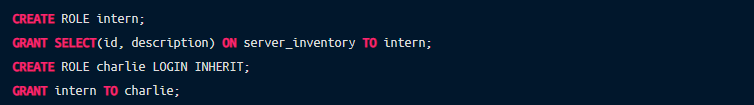
Other most commonly used database object privileges are INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE and TRUNCATE that correspond to the respective SQL statements, but you can also assign privileges for connecting to specific databases, creating new schemas or objects within the schema, executing functions and so on. Take a look at the Privileges section of PostgreSQL documentation to see the whole list.
One of the more advanced features of PostgreSQL privilege system is row-level security, which allows you to grant privileges to a subset of rows in a table. This includes both rows that can be queried with the SELECT statement, as well as rows that can be INSERTed, UPDATEd and DELETEd.
To start using row-level security, you need two things: enable it for a table and define a policy that will control row-level access.
Building on our previous example, let’s say that you want to allow users to update only their own servers. First, enable RLS on the table:
Without any policy defined, PostgreSQL defaults to the “deny” policy which means no role (other than the table owner which is typically the role that created the table) has any access to it.
A row security policy is a Boolean expression that PostgreSQL will evaluate for each row that is supposed to be returned or updated. The rows returned by SELECT statements are checked against the expression specified with the USING clause, while the rows updated by INSERT, UPDATE or DELETE statements are checked against the WITH CHECK expression.
Let’s define a couple of policies that allow users to see all servers but only update their own, as determined by the “owner” field of the table:

Note that only the owner of the table can create or update row security policies for it.
So far we have mostly talked about preemptive security measures. Following one of the cornerstone security principles, defense in depth, we have explored how they layer on top of each other to help slow down a hypothetical attacker’s progression through the system.
Keeping an accurate and detailed audit trail is one of the security properties of the system that is often overlooked. Monitoring the network-level or node-level access for your database server is out of scope of this post, but let’s take a look at what options we have when it comes to PostgreSQL server itself.
The most basic thing you can do to enhance visibility into what’s happening within the database is to enable verbose logging. Add the following directives to the server configuration file to turn on logging of all connection attempts and all executed SQL statements:
Unfortunately, this is pretty much the extent of what you can do with the standard self-hosted PostgreSQL installation out-of-the-box. It is better than nothing, of course, but it doesn’t scale well beyond a handful of database servers and simple “grepping” of log files.
For a more advanced PostgreSQL auditing solution, you can use a 3rd party extension such as pgAudit. You will have to install the extension manually if you’re using a self-hosted PostgreSQL instance. Some hosted versions such as AWS RDS support it out-of-the-box, so you just need to enable it.
pgAudit brings more structure and granularity to the logged statements. However, keep in mind that it is still logs-based, which makes it challenging to use if you want to ship your audit logs in structured format to an external SIEM system for detailed analysis.
Remoteler for Database Access is the open source project we built with the goal of helping you implement the best practices for securing your PostgreSQL (and other) databases that we discussed in this post.
As with any system designed with security in mind, properly guarding access to your database instance requires taking protective measures on multiple levels of the stack. One last check is make sure you’ve turned on data encryption, most cloud providers offer easy to use encryption solutions.
In this article we’ve taken a look at the best practices in protecting your PostgreSQL database access on multiple levels, starting with the network and transport security, and explored how to use PostgreSQL flexible user privilege system. Make sure to keep Postgres updated with the latest security patches and vulnerabilities.